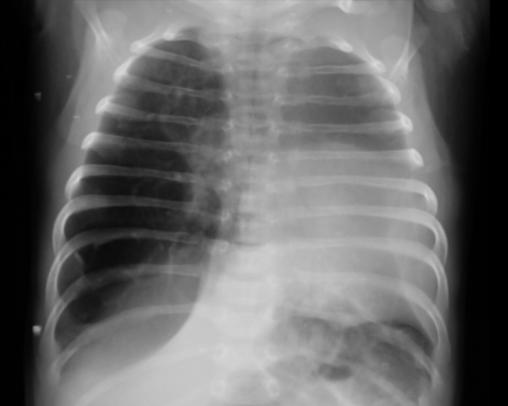
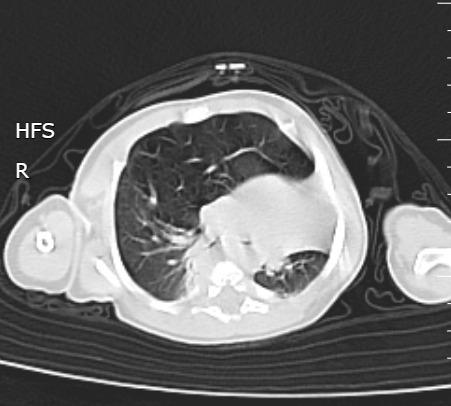
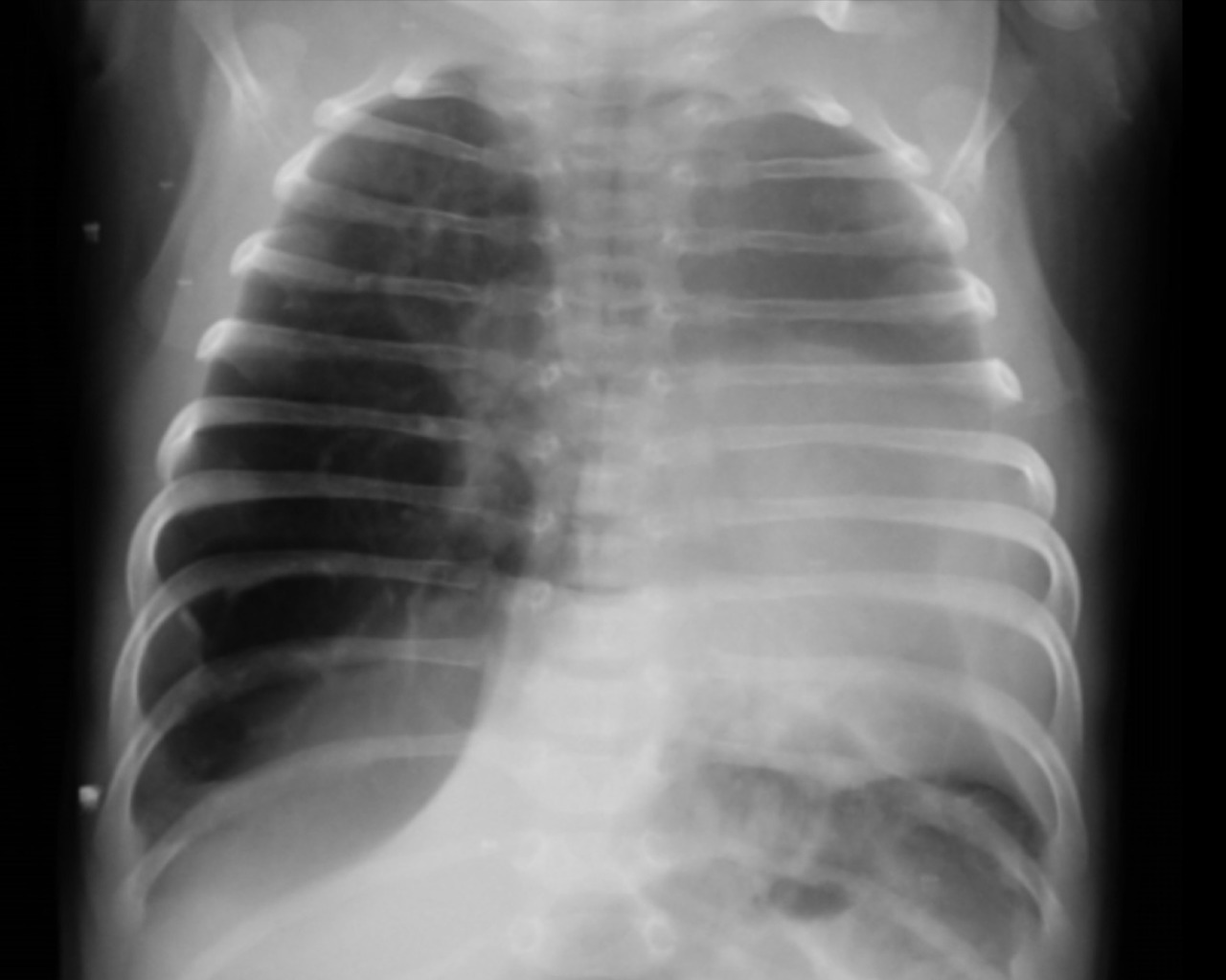
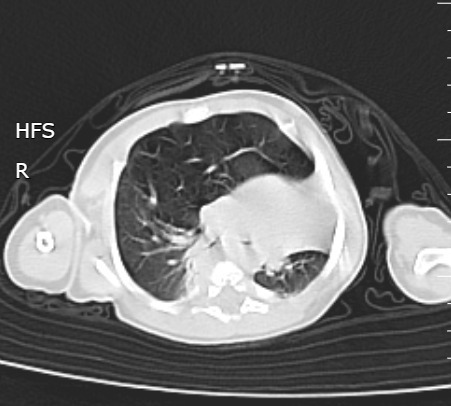
Un nouveau-né âgé de 1 mois est admis aux urgences pédiatriques pour prise en charge d’une détresse respiratoire. Le début de la symptomatologie remonte à la naissance, par l’installation d’une polypnée s’aggravant lors des cris et de l’alimentation, associée à des épisodes de toux sèche. L’examen clinique trouve un nouveau-né tachypnéique, cyanosé avec tirage intercostal et bombement de l’hémithorax droit associé à un wheezing auscultatoire et une SaO2 à 90 % à l’air ambiant. Le patient est mis sous oxygénothérapie et une radiographie thoracique est réalisée, objectivant une hyperaération de l’hémichamp pulmonaire droit refoulant le médiastin (fig. 1). Un scanner est effectué sans injection de produit de contraste et sans sédation, montrant une hyperclarté hypovasculaire avec une expansion du lobe supérieur gauche, refoulant le médiastin et la trachée à gauche, associée à une atélectasie du lobe inférieur droit et de l’hémichamp pulmonaire controlatéral (fig. 2). L’ensemble des éléments radio-cliniques plaident en faveur d’un emphysème lobaire géant compressif congénital (ELGC). Une lobectomie supérieure droite est réalisée, avec une bonne évolution clinique.
Références
1. Kerstine KH, Van Natta TL, Burkhart HM, et al. Congenital lung diseases. In Sabiston and Spencer's Surgery of the Chest. Saunders Elsevier Philadelphia 2010:129-50.
2. Bouhaouala MH, Charfi MR, Tlili K, et al. Giant lobar emphysema: The cause of compressive hemithoracic opacity in a newborn infant. Rev Mal Respir 1994;11(1):57-9.
3. Oliver ER, DeBari SE, Horii SC, et al. Congenital lobar overinflation: A rare enigmatic lung lesion on prenatal ultrasound an MRI. J Ultrasound Med 2019;38:1229-39.
4. Chia CC, Huang Sc, Liy MC. Fetal congenital lobar emphysema. J Obstet Gynecol 2007;46:73-6.
5. Pardes JG, Auh YH, Blomquist K, et al. Diagnosis of congenital lobar emphysema. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1983;7:1095-7.
6. Demir OF, Hangul M, Kose M. Congenital lobar emphysema: Diagnosis and treatment options. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2019;14:921-8.
7. Monin P, Didier F, Vert P, et al. Giant lobar emphysema neonatal diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 1979;8(4):259-60.
8. Desorgher G, Bayart M, Bayart R, et al. Giant lobar emphysema in the newborn: Left superior lobectomy. J Sci Med Lille 1970;88(1):39-45.
9. Hall NJ, Chiu PP, Langer JC. Morbidity after elective resection of prenatally diagnosed asymptomatic congenital pulmonary airway malformations. Pediatr Pulmonol 2015;2:1-6.
2. Bouhaouala MH, Charfi MR, Tlili K, et al. Giant lobar emphysema: The cause of compressive hemithoracic opacity in a newborn infant. Rev Mal Respir 1994;11(1):57-9.
3. Oliver ER, DeBari SE, Horii SC, et al. Congenital lobar overinflation: A rare enigmatic lung lesion on prenatal ultrasound an MRI. J Ultrasound Med 2019;38:1229-39.
4. Chia CC, Huang Sc, Liy MC. Fetal congenital lobar emphysema. J Obstet Gynecol 2007;46:73-6.
5. Pardes JG, Auh YH, Blomquist K, et al. Diagnosis of congenital lobar emphysema. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1983;7:1095-7.
6. Demir OF, Hangul M, Kose M. Congenital lobar emphysema: Diagnosis and treatment options. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2019;14:921-8.
7. Monin P, Didier F, Vert P, et al. Giant lobar emphysema neonatal diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 1979;8(4):259-60.
8. Desorgher G, Bayart M, Bayart R, et al. Giant lobar emphysema in the newborn: Left superior lobectomy. J Sci Med Lille 1970;88(1):39-45.
9. Hall NJ, Chiu PP, Langer JC. Morbidity after elective resection of prenatally diagnosed asymptomatic congenital pulmonary airway malformations. Pediatr Pulmonol 2015;2:1-6.
Une question, un commentaire ?
Lire aussi
Exercice